List of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Türkiye
Guide in Türkiye
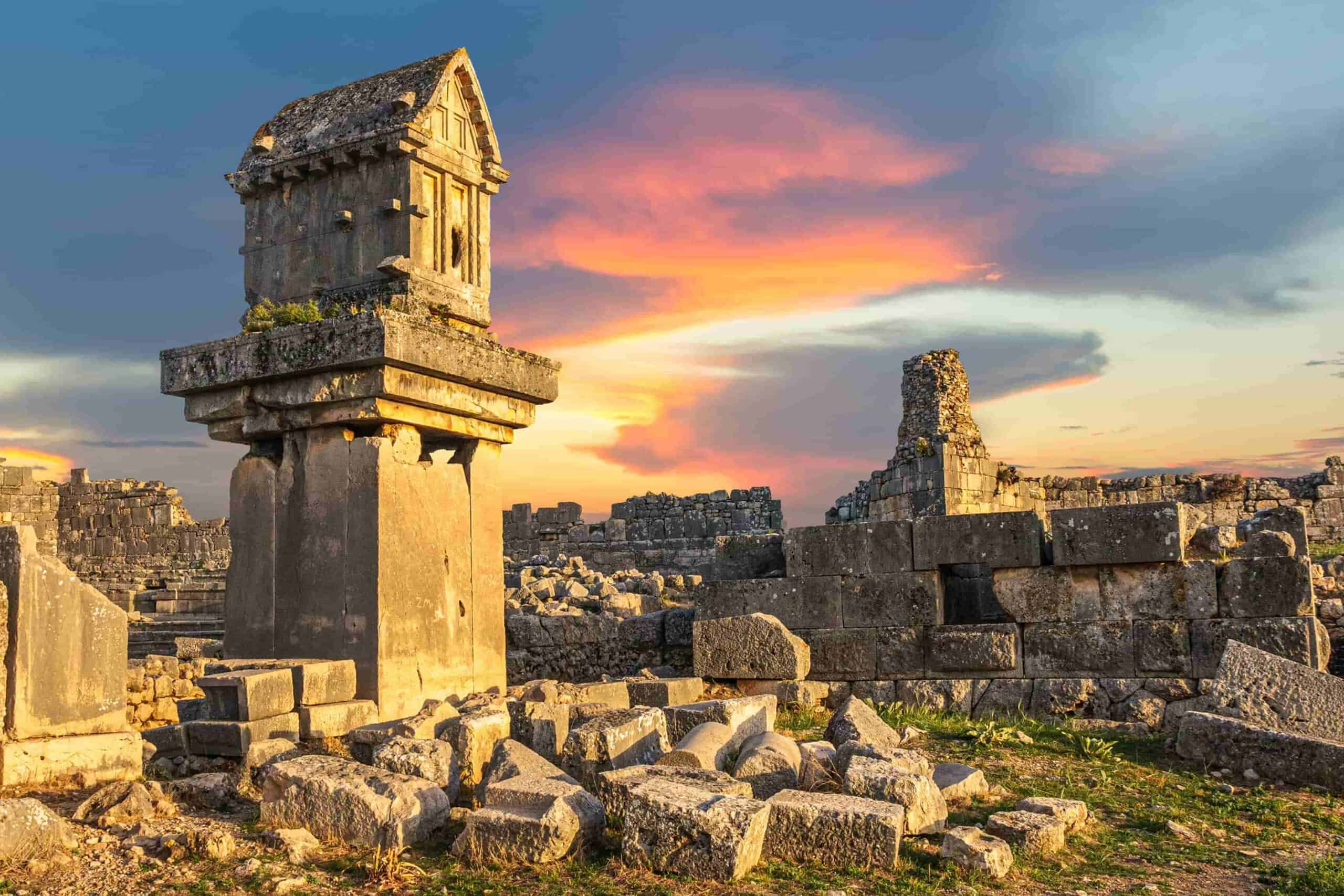

List of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Türkiye
Türkiye, rich in history, culture, and natural beauty, is home to an impressive array of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These sites, recognized for their universal cultural or natural significance, reflect the country's diverse heritage, spanning ancient civilizations, unique landscapes, and stunning architectural feats. From the ancient ruins of Ephesus to the fairy chimneys of Cappadocia, Türkiye offers a captivating journey through time. Whether you’re a history enthusiast, a nature lover, or someone fascinated by unique cultural practices, Türkiye’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites provide a glimpse into the country’s remarkable past and the need to preserve these treasures for future generations. In this blog, we will explore the diverse and iconic UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Türkiye, showcasing their importance and the stories they tell.
Overview of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Türkiye
Türkiye is a treasure trove of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, showcasing its rich cultural, historical, and natural diversity. With 21 sites currently on the UNESCO list, the country offers a unique blend of ancient ruins, architectural marvels, and breathtaking natural landscapes. Iconic locations like the ancient city of Troy, the well-preserved terraces of Pamukkale, and the rock-hewn churches of Cappadocia reflect the legacy of civilizations that thrived here for millennia. Cities like Istanbul feature landmarks such as Hagia Sophia and the Blue Mosque, which stand as testaments to the region's architectural brilliance and cultural evolution. Meanwhile, natural wonders like Göreme National Park demonstrate the harmonious blend of history and nature. Each site tells a story of Türkiye's unique position as a bridge between East and West, making it a must-visit destination for travelers and history enthusiasts alike.
History and Importance of each Heritage Site
Each UNESCO World Heritage Site in Türkiye holds a distinct historical significance and cultural importance, reflecting the country's rich and layered past. Sites like Ephesus, once a thriving ancient Greek and Roman city, showcase remarkable architectural achievements such as the Library of Celsus and the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Troy, immortalized in Homer’s epics, offers insight into early urban civilizations and their myths. Istanbul’s Historic Areas, including Hagia Sophia and Topkapi Palace, represent the confluence of Byzantine, Ottoman, and modern influences. The surreal terraces of Pamukkale and the ancient city of Hierapolis illustrate the integration of natural wonders with human ingenuity. Cappadocia’s Göreme National Park highlights unique geological formations and the early Christian monastic tradition. From the Neolithic settlement of Çatalhöyük to the Seljuk-era caravanserais of Anatolia, these sites narrate the evolution of human history and culture, making Türkiye a living museum of global heritage.
Best Times to Visit UNESCO World Heritage Sites
The best times to visit UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Türkiye largely depend on the region and your preferences for weather and crowds. Spring (April to June) and autumn (September to November) are ideal for most sites, offering mild temperatures and fewer tourists. During these seasons, you can explore the open-air wonders of Cappadocia, the terraces of Pamukkale, and the ruins of Ephesus comfortably. Coastal areas like Troy and Pergamon are particularly pleasant in late spring and early fall, avoiding the intense summer heat. Winter can be magical for sites like Cappadocia, where the fairy chimneys are dusted with snow, creating a surreal landscape. However, some high-altitude areas might be less accessible during colder months. Summer (July to August) is suitable for beachside locations but can be challenging for exploring historical ruins due to high temperatures. Planning your visit during the shoulder seasons ensures an enjoyable experience with optimal weather and more opportunities to immerse yourself in Türkiye’s rich heritage.
Conservation and Sustainability: Measures for Türkiye's UNESCO Heritage Sites
Conservation and sustainability are critical priorities for preserving Türkiye’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites, ensuring they remain intact for future generations. Measures include strict regulations to prevent urban sprawl and minimize the environmental impact around these sites. For example, authorities closely monitor tourism activities in areas like Cappadocia and Pamukkale to control overcrowding and reduce wear on delicate landscapes. Advanced restoration techniques are employed to maintain the structural integrity of ancient ruins such as Ephesus and Troy. Public awareness campaigns also play a significant role, in educating locals and visitors about the importance of heritage conservation. Additionally, Türkiye collaborates with international organizations to secure funding and expertise for sustainable preservation efforts. These measures ensure that the cultural and natural treasures of Türkiye continue to reflect their historical significance while adapting to modern-day challenges.